Heart Conditions
Patient Education
This portion of our website provides information about specific types of congenital heart disease. These are the most common heart conditions. Below are just some of the heart conditions we care for.
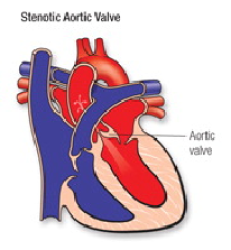
Aortic Valve Stenosis
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)

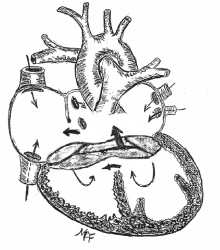
Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD)
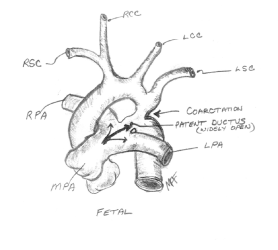
Coarctation of the Aorta
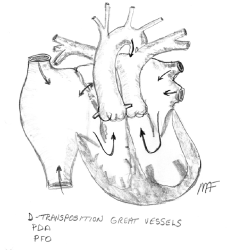
D-Transposition of the Great Arteries
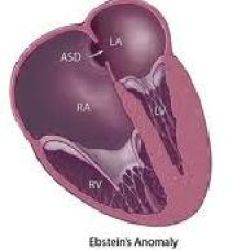
Ebstein's Anomaly
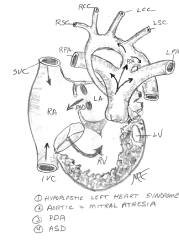
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)
L-Transposition of the Great Arteries (Ventricular Inversion)
A heart in which the lower section is fully reversed.

Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
An unclosed hole in the aorta.

Pulmonary Atresia with Intact Ventricular Septum
The pulmonary valve does not exist, and the only blood receiving oxygen is the blood that is diverted to the lungs through openings that normally close during development.

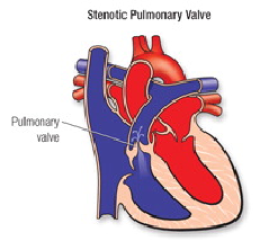
Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
A thickened or fused heart valve that does not fully open. The pulmonary valve allows blood to flow out of the heart, into the pulmonary artery and then to the lungs.
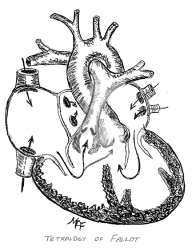
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
A heart defect that features four problems. They are: a hole between the lower chambers of the heart an obstruction from the heart to the lungs The aorta (blood vessel) lies over over the hole in the lower chambers The muscle surrounding the lower right chamber becomes overly thickened.
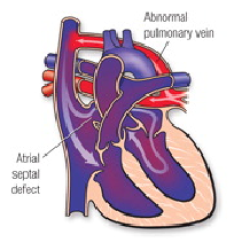
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection (TAPVC)
A defect in the veins leading from the lungs to the heart. In TAPVC, the blood does not take the normal route from the lungs to the heart and out to the body. Instead, the veins from the lungs attach to the heart in abnormal positions and this problem means that oxygenated blood enters or leaks into the wrong chamber.
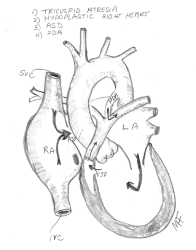
Tricuspid Atresia
There is no tricuspid valve in the heart so blood cannot flow from the body into the heart in the normal way. The blood is not being properly refilled with oxygen it does not complete the normal cycle of body -heart –lungs- heart - body.
Truncus Arteriosus
When a person has one large artery instead of two separate ones to carry blood to the lungs and body.
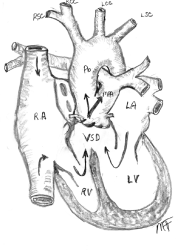
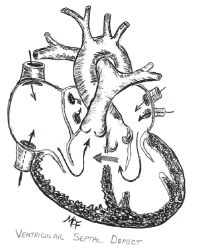
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
VSD is a hole in the wall separating the two lower chambers of the heart.